
-
英国IQD晶振|HC49/4HSMX|LFXTAL081958Reel|SMD晶振
更多 +英国IQD晶振|HC49/4HSMX|LFXTAL081958Reel|SMD晶振,英国IQD晶振,HC49/4HSMX无源晶振,SMD晶振,LFXTAL081958Reel晶振,石英晶体谐振器,13.4×4.9mm晶振,49S贴片晶振,二脚封装晶振,频率28.636363MHz,负载30pF,频率容差30ppm,工作温度-40~85°C,行业标准低成本SMD版本,采用电阻焊接,在惰性气体中密封,引线上的玻璃与金属密封,家用电视机顶盒晶振,随身听晶振,数码产品晶振,物联网晶振.

-
IQD晶振|4SMX|LFXTAL029659Reel|5032mm晶振
更多 +IQD晶振|4SMX|LFXTAL029659Reel|5032mm晶振,欧美进口晶振,IQD晶振,4SMX无源晶振,陶瓷晶振,LFXTAL029659Reel 晶振,石英晶体谐振器,贴片晶体,5032mm晶振,SMD晶振,二脚封装晶振,频率14.7456MHz,负载30pF,频率容差50ppm,工作温度-10~60°C,高密封晶振,低老化晶振,无铅环保晶振,寻呼机晶振,移动电话晶振,键盘鼠标晶振,家用电器遥控器晶振.

-
Anderson晶振|AE-232-A-1-4085-2-30-48M0000|6032mm|通信设备晶振
Anderson晶振|AE-232-A-1-4085-2-30-48M0000|6032mm|通信设备晶振,Anderson晶振,欧美进口晶振,AE232无源晶振,SMD晶体, AE-232-A-1-4085-2-30-48M0000晶振,6032mm晶振,石英晶体谐振器,四脚贴片晶振,石英晶振,频率48MHz,负载30pF,频率容差10ppm,紧凑薄晶振,高可靠性晶振,低老化晶振,通信设备晶振,工业设备晶振,传呼机晶振,蜂窝电话晶振.更多 +
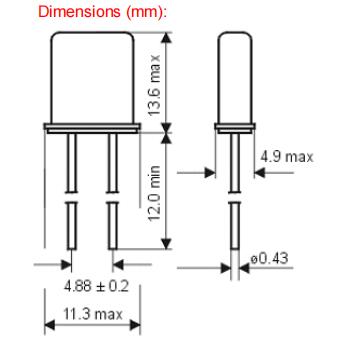
-
12.81119|10MHz|30pF|进口插件晶振|GEYER CRYSTAL
更多 +12.81119|10MHz|30pF|进口插件晶振|GEYER CRYSTAL,欧美晶振,GEYER CRYSTAL,KX-49T石英晶振,进口插件晶振,12.81119晶振,无源晶振,HC-49/U晶振,晶体谐振器,二脚封装晶振,频率10MHz,负载30pF,工作温度-40~85°C,频率容差30ppm,小体积晶振,高稳定性晶振,低老化晶振,专业视频设备晶振,移动电话晶振,无线局域网晶振,家用电视机顶盒晶振.

-
12.81110|16MHz|30pF|HC-49/U晶振|格耶晶振
更多 +12.81110|16MHz|30pF|HC-49/U晶振|格耶晶振,格耶晶振,KX-49T进口晶振,无源晶振,12.81110晶振,二脚插件晶振,HC-49/U晶振,石英晶体谐振器,频率16MHz,负载30pF,工作温度-40~85°C,频率容差30ppm,高可靠性晶振,抗冲击晶振,无铅环保晶振,USB存储设备晶振,网络终端晶振,电子体重秤晶振,血压计晶振.

-
12.81078|KX-49T|5.0688MHz|30pF|GEYER晶振
更多 +12.81078|KX-49T|5.0688MHz|30pF|GEYER晶振,欧美进口晶振,GEYER晶振,KX-49T无源晶振,插件晶振,12.81078晶振,石英晶体谐振器,二脚封装晶振,频率5.06880MHz,负载30pF,工作温度-40~85°C,频率容差50ppm,无铅环保晶振,高品质晶振,低老化晶振,录音笔晶振,DVD家电影音系统晶振,随身听晶振,监控摄像头晶振.
- [行业新闻]ABS07W-32.768KHZ-J-2-T音叉晶体可实现最佳的电路内性能2023年04月25日 08:44
Abracon开发了分别为2.0x1.2x0.6毫米和3.2x1.5x0.9毫米的ABS06W和ABS07W系列音叉晶体时,为了实现最佳的电路内性能,Abracon优化了电极图案,以减少C0的总体影响,使得2.0x1.2x0.6mm封装的最大保证(电极+封装)电容为2.0pF,石英晶振3.2x1.5x0.9mm封装的最高保证电容为1.30pF。凭借革命性的坯料设计和加工技术,Abracon能够大幅降低这些解决方案的ESR,工作温度范围为-40°C至+125°C;同时将电镀负载降低到行业领先的3.0pF。
特征:3.0pF的极低电镀负载,是可穿戴设备的理想选择,无线和物联网应用,在延长运行期间同时优化ESR,小体积无源晶振3.2x1.5x0.9mm SMD封装,非常适合空间受限设计,可提供±10 ppm的设定公差,接缝密封包装,具有长期可靠性
ABS07W-32.768KHZ-J-2-T音叉晶体可实现最佳的电路内性能
应用于:可穿戴设备,无线模块,物联网(IoT),蓝牙/蓝牙低能耗(BLE),机器对机器(M2M)连接,超低功耗MCU,近场通信(NFC),ISM频段应用,超低功耗节能MCU。- 阅读(799)
- [行业新闻]Resonators的各项参数及性能2019年11月05日 14:39
石英晶体谐振器在电子学中的重要性在于其极高的Q值、相对较小的尺寸和优异的温度稳定性。
石英晶体谐振器利用石英的压电特性直接压电效应是指机械应力作用下某些材料产生的电极化效应。逆效应是指同一材料在电场作用下产生的变形。
在石英晶体谐振器中,在两个电极之间放置一薄片石英,其相对于晶体轴以适当的方向切割。施加在这些电极上的交流电压会使石英同时振动。伴随而来的极化变化构成了通过谐振器的电位移电流。
当外加电压的频率接近石英薄片的机械共振频率之一时,振动的振幅变得很大。伴随的位移电流也会增大,因此器件的有效阻抗会减小。在石英晶体谐振器作为晶体振荡器的频率控制元件的应用中,阻抗随共振附近频率的变化而迅速变化是关键因素。
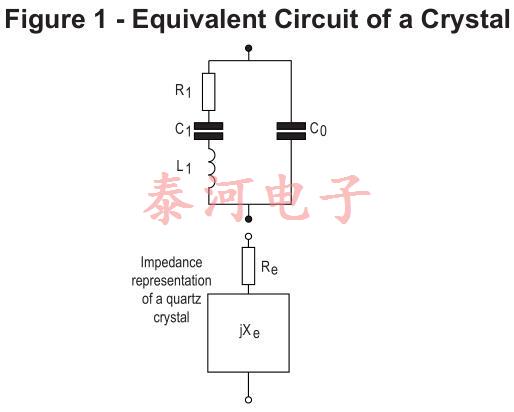
在电气方面,石英晶体可以用图1中的等效电路表示,其中串联组合r1、l1和c1表示压电效应对阻抗的贡献,c0表示电极之间的并联电容以及任何杂散保持器电容。电感l1是石英质量的函数,而电容c1与其刚度相关。电阻r1是石英和安装装置损耗的结果。等效电路的参数测量精度可达1%左右。
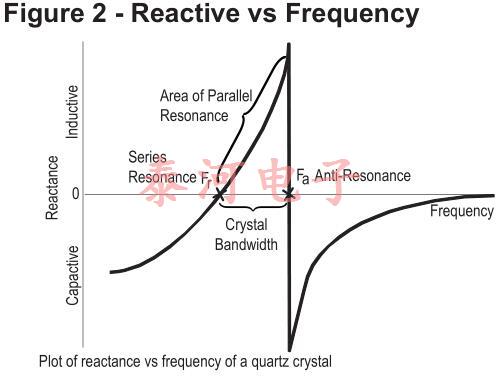
等效电路的电抗频率图如图2所示。晶振性能的相关公式有很多,其中第一个是fs。这是晶体串联共振的频率,由下式给出:
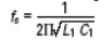
其中fs以赫兹表示,l1以亨利表示,c1以法拉表示。
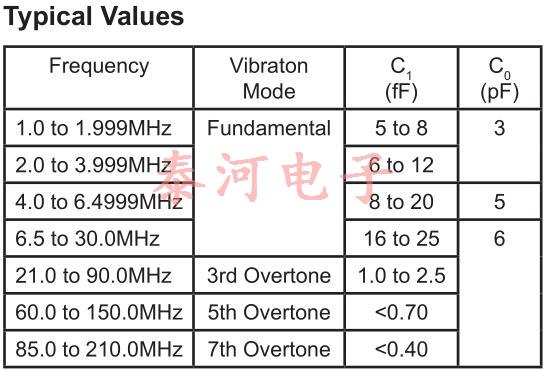
典型晶体参数值
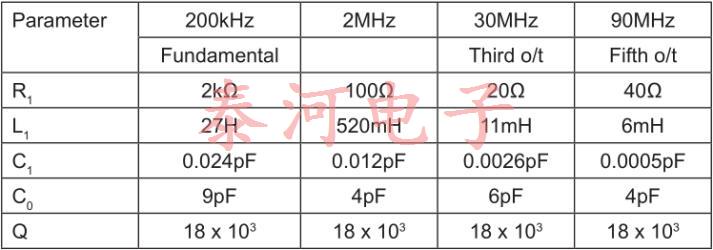
校准公差
校准公差是晶体在特定温度、基准温度(通常为25°C)下频率的最大允许偏差。
频率稳定性
晶振不稳定有多种原因。温度变化和质量的物理变化导致了我们称之为老化的长期漂移,这可能是我们最关心的问题。
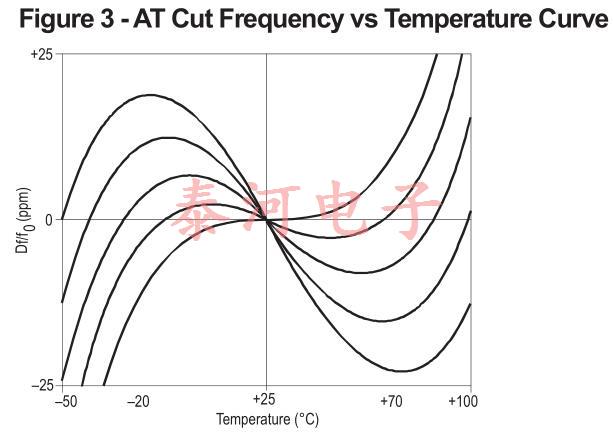
通过适当选择晶振切割和(对于严格的公差要求)在晶振电路中包括与温度相关的电抗,或在小烤箱中保持恒定温度,可将温度变化的影响降至最低。at-cut晶体是当今应用最广泛的晶振,因为它们的频率-温度曲线家族很容易以低成本为所有应用(除了最苛刻的应用)提供良好的性能。
未补偿的AT切割晶体可以在-10°C到60°C的范围内规定公差为±5ppm,更宽的温度范围需要更大的公差,如图3所示,显示了AT切割频率温度曲线的典型系列这些曲线可以用三次方程表示,并且强烈依赖于石英坯料的切割角度零温度系数的点称为上下拐点通过选择切割角度,可以将一个转折点放置在需要的位置;然后固定另一个转折点,因为这两个转折点在20°~30°C范围内的某个点上是对称的。转弯点之间的坡度随着它们一起移动而变小。设计用于烘箱的晶体被切割,以便上转折点与烘箱工作温度一致。
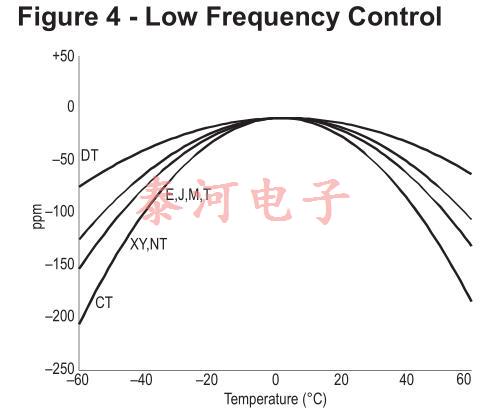
图4显示了几个低频切割的频率-温度曲线。J-cut在10kHz以下使用,而XY-cut可以在3kHz到85kHz之间使用。可在10KHz范围内使用NT切割。dt-cut适用于100khz至800khz左右,ct-cut适用于300khz至900khz。
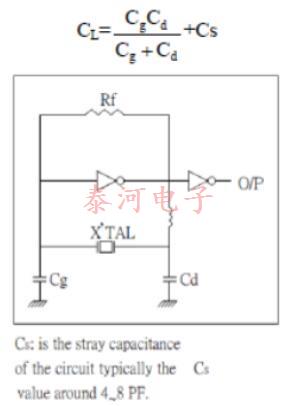
负载电容
晶振可以由其制造商在fr处进行校准,在fr处它们看起来是电阻的(或非常接近fr的fs),或者在与电容性负载共振时,它们当然必须是电感的。后一种情况称为负载共振,通常用符号fl表示;更具体地说,符号f30,例如,表示晶体与30pF电容性负载共振的频率。

晶体电抗曲线上需要校准的点由电路结构决定一般来说,振荡器中的非反相保持放大器需要在fr处校准,而反相放大器需要在“负载电容”cl的某个值处校准。后一种配置依赖于电感晶体以及与之共振的负载电容,提供180度的相位偏移。
该规则最常见的例外是,当小电容器(例如变容二极管)与非反相放大器电路中的晶体串联以提供一定程度的频率调整时。在这种情况下,必须用电容的平均值校准晶体的共振。
可拉性
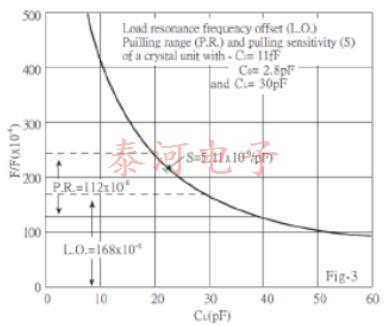
晶体的可拉性是在给定的负载电容变化下测量其频率变化的一种方法。这通常表示为串联谐振频率(fr)和负载谐振频率(fL)之间的差异该偏移量可使用分数负载谐振频率偏移量(dl)以百万分之几计算,即给定值cl时,从fr到fl的实际频率变化。
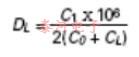
其中C1,C0和CL均以相同单位表示。图5显示了频率变化相对于负载电容变化的影响的典型曲线。

另外,通常将晶体的可拉性表示为修整灵敏度,单位为ppm / pF负载电容变化。 通过ppm / pF给出:
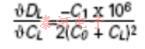
其中C1,C0和CL以pF为单位,并且在图6中以图形方式显示了(C0 + CL)的各种值。
- 阅读(491)
- [行业新闻]Crystal parameters description2019年10月29日 10:37
About Crystal parameters description,Crystal Project Name
AT Cut Crystals
For precise frequency control in radio and line communication systems, quartz crystal resonators have proved indispensable. The material properties of crystalline quartz are such that quartz resonators display stableness and Q factors that cannot be matched by other types of resonator over the frequency range from 1 MHz to 200 MHz.
Equivalent Circuit
Fig-1 shows the conventionally accepted equivalent circuit of a crystal resonator at a frequency near its main mode of vibration. The inductance LI reiperesents the vibrating mass, the series capacitance CL the compliance of the quartz element and the resistance Rl the internal frication of the element, mechanical losses in the mounting system and acoustical losses to the surrounding environment.
The shunt capacitance Co is made up of the static capacitance between the electrodes, togettier with stray capacitances of the mounting system.
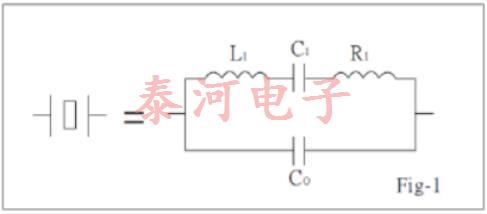
There are two zero-phase frequencies associated with this simple circuit, one is at series resonance fs, another at antiresonance fa. When used in an oscillator, crystal units will operate at any frequency within the broken lines of Fig-2 as determined by the phase of the maintaining circuit.
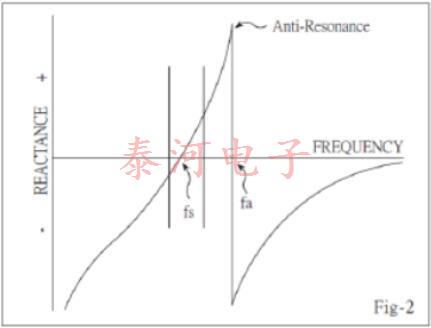
By changing of this reactive condition, the crystal frequency may be trimmed in a limited extent. The degree to which this frequency may be varied (frequency pulling) is inversely proportional to the capacitance ratio r(C〇 /Ci).
Load Capacitance
Many practical oscillator circuits make use of a load capacitor CL in series or parallel with the crystal, either in order to provide a means for final frequency adjustment, or perhaps for modulation or temperature compensation purposes. For the crystal load capacitance. We looking into the circuit through the two crystal terminals, the load capacitance need to specified when the crystal is paralleled mode, crystal load capacitance is calculated as below:
Frequency Pulling
In many applications a variable capacitor (trimmer) is used as the load reactive element to adjust the frequency. The fractional frequency range available between specified values of this load reactive element is called the pulling range (PR.) and it can be calculated by using the following formula:

Sensitivity
A useful parameter to the design engineer is the pulling sensitivity (S) at a specified value of load capacitance. It is defined as the incremental fractional frequency change for an incremental change in load capacitance. It is normally expressed in ppm/pF (10-6/pF) and can be calculated from the formula:

It is very important to define the mean load capacitance to enable the actual crystal frequency be set within the tolerances of the specified nominal frequency. It is also important to use, wherever possible, standard values of load capacitance; for example:20pF, 30pF.
Fig-3 shows the relationship between LO.; P.R. and S.
Frequency Pulling Calculation
An approximation to the pulling for any crystal can be calculated from this simple formula:

Resistance
The equivalent circuit of the crystal has one other important parameter: This is Ri, the motional resistance. This parameter controls the Q of the crystal unit and will define the level of oscillation in any maintaining circuit. The load resonance for a given crystal unit depends upon the load capacitance with which that unit is intended to operate. The frequency of oscillation is the same in either series or parallel connection of the load capacitance.
If the external capacitance is designated the load resonance resistance may be calculated as follows:

The equivalent shunt or parallel resistance at load resonance frequency is approximately:
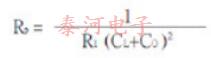
It should be remembered that Ri does not change thus the effective parameters of any user network can be readily calculated.
Frequency Temperature Characteristics
The AT-cut crystal has a frequency temperature characteristic which may be described by a cubic function of temperature. This characteristic can be precisely controlled by small variations in the exact angle at which the crystal blank is cut from the original quartz bar. Fig,4 illustrates some typical cases. This cubic behaviour is in contrast to most other crystal cuts, which have parabolic temperature characteristics.
As a consequence, the AT-cut is generally the best choice when specifying a unit to operate over a wide temperature range, and is available in a range of frequencies from 1 to 200 MHz.

- 阅读(250)
- [行业新闻]泰艺厂家为你介绍几个晶振知识2018年05月04日 11:59
Cstray电路中的寄生电容,通常2-5pF,Ci和公司外部电容器在振荡器电路.CL电路中必须尽可能接近16 pf达到指定的输出频率.如果指定的振荡频率高于,电容器的值应该增加到更低的频率.另一方面,如果频率低于指定,电容值需要提高输出频率降低.当CL = 16 pf,C1和公司将大约22-30pF,加上额外的寄生电容.C1和的值用于电路有限公司将会有很大的影响CL输出频率的影响.
- 阅读(275)
相关搜索
热点聚焦
- 1时钟振荡器XO57CTECNA12M电信设备专用晶振
- 2汽车音响控制器专用晶振403C35D28M63636
- 3XCO时钟振荡器C04310-32.000-EXT-T-TR支持微控制器应用
- 4ABS07W-32.768KHZ-J-2-T音叉晶体可实现最佳的电路内性能
- 5402F24011CAR非常适合支持各种商业和工业应用
- 6无线模块专用微型ECS-240-8-36-TR晶体
- 7DSX321G晶体谐振器1N226000AA0G汽车电子控制板专用晶振
- 8lora模块低功耗温补晶振ECS-327TXO-33-TR
- 9ECS-250-12-33QZ-ADS-TR适合高冲击和高振动环境的理想选择
- 10ECS-200-20-20BM-TR紧凑型SMD晶体是物联网应用的理想选择
 泰河盛微信号
泰河盛微信号

 在线留言
在线留言 收藏网站
收藏网站 网站地图
网站地图
 手机版
手机版
 全球咨询热线:
全球咨询热线:
 快速通道
快速通道
